Complete code for a Spring OAuth2 implementation of Multi-Factor Authentication has been uploaded to a file sharing site at this link. Instructions are given below to recreate the current problem on any computer in only a few minutes.
**CURRENT PROBLEM:**
Most of the authentication algorithm works correctly. The program does not break until the very end of the control flow shown below. Specifically, an `Invalid CSRF token found for http://localhost:9999/uaa/oauth/token` error is being thrown at the end of the **SECOND PASS** below. The app in the link above was developed by adding a custom `OAuth2RequestFactory`, `TwoFactorAuthenticationFilter` and `TwoFactorAuthenticationController` to the `authserver` app of this Spring Boot OAuth2 GitHub sample. **What specific changes need to be made to the code below in order to resolve this CSRF token error and enable 2-factor authentication?**
My research leads me to suspect that the `CustomOAuth2RequestFactory` (API at this link) might be the place to configure a solution because it defines ways for managing `AuthorizationRequest`s and `TokenRequest`s.
**This section of the official OAuth2 spec indicates that the `state` parameter of the request made to the authorization endpoint is the place where the `csrf` token is added.**
Also, the code in the link uses the Authorization Code Grant Type described at this link to the official spec, which would mean that Step C in the flow does not update the `csrf` code, thus triggering the error in Step D. (You can view the entire flow including Step C and Step D in the official spec.)
**CONTROL FLOW SURROUNDING THE CURRENT ERROR:**
The current error is being thrown during the **SECOND PASS** through `TwoFactorAuthenticationFilter` in the flowchart below. Everything works as intended until the control flow gets into the **SECOND PASS**.
The following flowchart illustrates the control flow of the two factor authentication process that is employed by the code in the downloadable app.
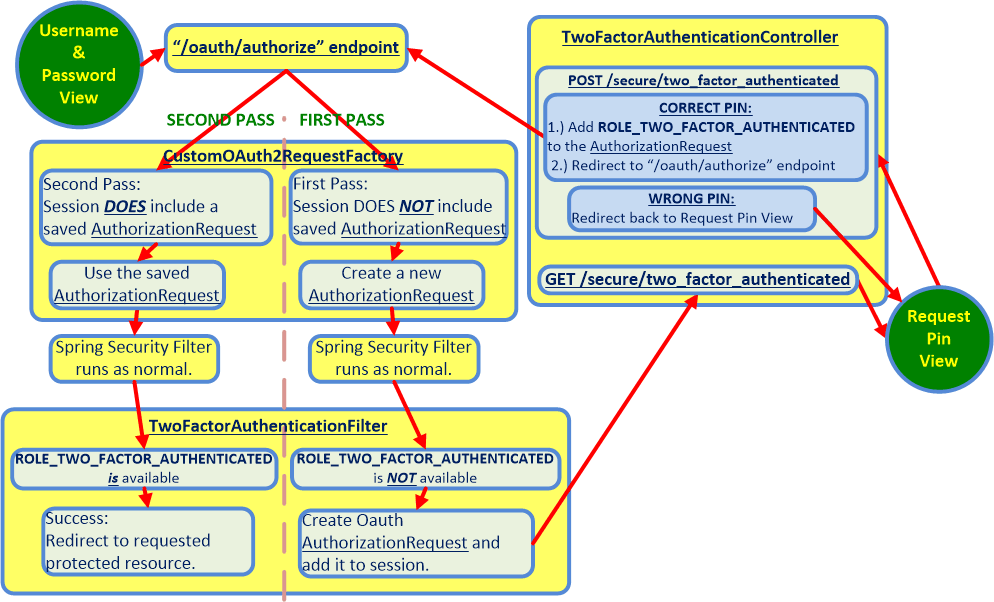
Specifically, the Firefox `HTTP` Headers for the sequence of `POST`s and `GET`s show that the same `XSRF` cookie is sent with every request in the sequence. The `XSRF` token values do not cause a problem until after the `POST /secure/two_factor_authentication`, which triggers server processing at the `/oauth/authorize` and `/oauth/token` endpoints, with `/oauth/token` throwing the `Invalid CSRF token found for http://localhost:9999/uaa/oauth/token` error.
To understand the relationship between the above control flow chart and the `/oauth/authorize` and `/oauth/token` endpoints, you can compare the above flowchart side by side with the chart for the single factor flow at the official spec in a separate browser window. The **SECOND PASS** above simply runs through the steps from the one-factor official spec a second time, but with greater permissions during the **SECOND PASS**.
**WHAT THE LOGS SAY:**
The HTTP Request and Response Headers indicate that:
1.) A POST to `9999/login` with the correct `username` and `password` submitted results in a redirect to `9999/authorize?client_id=acme&redirect_uri=/login&response_type=code&state=sGXQ4v` followed by a `GET 9999/secure/two_factor_authenticated`. One XSRF token remains constant across these exchanges.
2.) A POST to `9999/secure/two_factor_authentication` with the correct pin code sends the same `XSRF` token, and gets successfully re-directed to `POST 9999/oauth/authorize` and makes it into `TwoFactorAuthenticationFilter.doFilterInternal()` and proceeds to `request 9999/oauth/token`, but `9999/oauth/token` rejects the request because the same old XSRF token does not match a new `XSRF` token value, which was apparently created during the **FIRST PASS**.
One obvious difference between `1.)` and `2.)` is that the second `request 9999/oauth/authorize` in `2.)` does not contain the url parameters which are included in the first request to `9999/authorize?client_id=acme&redirect_uri=/login&response_type=code&state=sGXQ4v` in `1.)`, and also defined in the official spec. But it is not clear if this is causing the problem.
Also, it is not clear how to access the parameters to send a fully formed request from the `TwoFactorAuthenticationController.POST`. I did a SYSO of the `parameters` `Map` in the `HttpServletRequest` for the `POST 9999/secure/two_factor_authentication` controller method, and all it contains are the `pinVal` and `_csrf` variables.
You can read all the HTTP Headers and Spring Boot logs at a file sharing site by clicking on this link.
**A FAILED APPROACH:**
I tried @RobWinch's approach to a similar problem in the Spring Security 3.2 environment, but the approach does not seem to apply to the context of Spring OAuth2. Specifically, when the following `XSRF` update code block is uncommented in the `TwoFactorAuthenticationFilter` code shown below, the downstream request headers do show a different/new `XSRF` token value, but the same error is thrown.
if(AuthenticationUtil.hasAuthority(ROLE_TWO_FACTOR_AUTHENTICATED)){
CsrfToken token = (CsrfToken) request.getAttribute("_csrf");
response.setHeader("XSRF-TOKEN"/*"X-CSRF-TOKEN"*/, token.getToken());
}
**This indicates that the `XSRF` configuration needs to be updated in a way that `/oauth/authorize` and `/oauth/token` are able to talk with each other and with the client and resource apps to successfully manage the `XSRF` token values.** Perhaps the `CustomOAuth2RequestFactory` is what needs to be changed to accomplish this. But how?
**RELEVANT CODE:**
The code for `CustomOAuth2RequestFactory` is:
public class CustomOAuth2RequestFactory extends DefaultOAuth2RequestFactory {
public static final String SAVED_AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME = "savedAuthorizationRequest";
public CustomOAuth2RequestFactory(ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService) {
super(clientDetailsService);
}
@Override
public AuthorizationRequest createAuthorizationRequest(Map authorizationParameters) {
ServletRequestAttributes attr = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
HttpSession session = attr.getRequest().getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest = (AuthorizationRequest) session.getAttribute(SAVED_AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME);
if (authorizationRequest != null) {
session.removeAttribute(SAVED_AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME);
return authorizationRequest;
}
}
return super.createAuthorizationRequest(authorizationParameters);
}
}
The code for `TwoFactorAuthenticationFilter` is:
//This class is added per: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/30319666/two-factor-authentication-with-spring-security-oauth2
/**
* Stores the oauth authorizationRequest in the session so that it can
* later be picked by the {@link com.example.CustomOAuth2RequestFactory}
* to continue with the authoriztion flow.
*/
public class TwoFactorAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
private OAuth2RequestFactory oAuth2RequestFactory;
//These next two are added as a test to avoid the compilation errors that happened when they were not defined.
public static final String ROLE_TWO_FACTOR_AUTHENTICATED = "ROLE_TWO_FACTOR_AUTHENTICATED";
public static final String ROLE_TWO_FACTOR_AUTHENTICATION_ENABLED = "ROLE_TWO_FACTOR_AUTHENTICATION_ENABLED";
@Autowired
public void setClientDetailsService(ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService) {
oAuth2RequestFactory = new DefaultOAuth2RequestFactory(clientDetailsService);
}
private boolean twoFactorAuthenticationEnabled(Collection authorities) {
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>> List of authorities includes: ");
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) {
System.out.println("auth: "+authority.getAuthority() );
}
return authorities.stream().anyMatch(
authority -> ROLE_TWO_FACTOR_AUTHENTICATION_ENABLED.equals(authority.getAuthority())
);
}
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("------------------ INSIDE TwoFactorAuthenticationFilter.doFilterInternal() ------------------------");
// Check if the user hasn't done the two factor authentication.
if (AuthenticationUtil.isAuthenticated() && !AuthenticationUtil.hasAuthority(ROLE_TWO_FACTOR_AUTHENTICATED)) {
System.out.println("++++++++++++++++++++++++ AUTHENTICATED BUT NOT TWO FACTOR +++++++++++++++++++++++++");
AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest = oAuth2RequestFactory.createAuthorizationRequest(paramsFromRequest(request));
/* Check if the client's authorities (authorizationRequest.getAuthorities()) or the user's ones
require two factor authenticatoin. */
System.out.println("======================== twoFactorAuthenticationEnabled(authorizationRequest.getAuthorities()) is: " + twoFactorAuthenticationEnabled(authorizationRequest.getAuthorities()) );
System.out.println("======================== twoFactorAuthenticationEnabled(SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getAuthorities()) is: " + twoFactorAuthenticationEnabled(SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getAuthorities()) );
if (twoFactorAuthenticationEnabled(authorizationRequest.getAuthorities()) ||
twoFactorAuthenticationEnabled(SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getAuthorities())) {
// Save the authorizationRequest in the session. This allows the CustomOAuth2RequestFactory
// to return this saved request to the AuthenticationEndpoint after the user successfully
// did the two factor authentication.
request.getSession().setAttribute(CustomOAuth2RequestFactory.SAVED_AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, authorizationRequest);
// redirect the the page where the user needs to enter the two factor authentiation code
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response,
ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentContextPath()
.path(TwoFactorAuthenticationController.PATH)
.toUriString());
return;
}
}
//THE NEXT "IF" BLOCK DOES NOT RESOLVE THE ERROR WHEN UNCOMMENTED
//if(AuthenticationUtil.hasAuthority(ROLE_TWO_FACTOR_AUTHENTICATED)){
// CsrfToken token = (CsrfToken) request.getAttribute("_csrf");
// this is the value of the token to be included as either a header or an HTTP parameter
// response.setHeader("XSRF-TOKEN", token.getToken());
//}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
private Map paramsFromRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map params = new HashMap();
for (Entry entry : request.getParameterMap().entrySet()) {
params.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()[0]);
}
return params;
}
}
**RE-CREATING THE PROBLEM ON YOUR COMPUTER:**
You can recreate the problem on any computer in only a few minutes by following these simple steps:
1.) Download the zipped version of the app from a file sharing site by clicking on this link.
2.) Unzip the app by typing: `tar -zxvf oauth2.tar(2).gz`
3.) launch the `authserver` app by navigating to `oauth2/authserver` and then typing `mvn spring-boot:run`.
4.) launch the `resource` app by navigating to `oauth2/resource` and then typing `mvn spring-boot:run`
5.) launch the `ui` app by navigating to `oauth2/ui` and then typing `mvn spring-boot:run`
6.) Open a web browser and navigate to `http : // localhost : 8080`
7.) Click `Login` and then enter `Frodo` as the user and `MyRing` as the password, and click to submit.
8.) Enter `5309` as the `Pin Code` and click submit. **This will trigger the error shown above.**
You can view the complete source code by:
a.) importing the maven projects into your IDE, or by
b.) navigating within the unzipped directories and opening with a text editor.
You can read all the HTTP Headers and Spring Boot logs at a file sharing site by clicking on this link.
What is an invalid CSRF token?
Invalid or missing CSRF token This error message means that your browser couldn't create a secure cookie, or couldn't access that cookie to authorize your login. This can be caused by ad- or script-blocking plugins, but also by the browser itself if it's not allowed to set cookies.
How do I get my CSRF token?
To fetch a CRSF token, the app must send a request header called X-CSRF-Token with the value fetch in this call. The server generates a token, stores it in the user's session table, and sends the value in the X-CSRF-Token HTTP response header.
What does CSRF token mean?
A CSRF token is a secure random token (e.g., synchronizer token or challenge token) that is used to prevent CSRF attacks. The token needs to be unique per user session and should be of large random value to make it difficult to guess. A CSRF secure application assigns a unique CSRF token for every user session.
One idea that popped to my head:
If session fixation is activated, a new session is created after the user authenticated successfully (see SessionFixationProtectionStrategy). This will also of course create a new csrf token if you use the default HttpSessionCsrfTokenRepository. Since you're mentioning the XSRF-TOKEN header I assume you use some JavaScript frontend. I could imagine that the original csrf token that was used for the login is stored and reused afterwards - which would not work because this csrf token is not valid anymore.
You may try disabling session fixation (http.sessionManagement().sessionFixation().none() or <session-management session-fixation-protection="none"/>) or re-get the current CSRF token after login.
 Specifically, the Firefox `HTTP` Headers for the sequence of `POST`s and `GET`s show that the same `XSRF` cookie is sent with every request in the sequence. The `XSRF` token values do not cause a problem until after the `POST /secure/two_factor_authentication`, which triggers server processing at the `/oauth/authorize` and `/oauth/token` endpoints, with `/oauth/token` throwing the `Invalid CSRF token found for http://localhost:9999/uaa/oauth/token` error.
To understand the relationship between the above control flow chart and the `/oauth/authorize` and `/oauth/token` endpoints, you can compare the above flowchart side by side with the chart for the single factor flow at the official spec in a separate browser window. The **SECOND PASS** above simply runs through the steps from the one-factor official spec a second time, but with greater permissions during the **SECOND PASS**.
Specifically, the Firefox `HTTP` Headers for the sequence of `POST`s and `GET`s show that the same `XSRF` cookie is sent with every request in the sequence. The `XSRF` token values do not cause a problem until after the `POST /secure/two_factor_authentication`, which triggers server processing at the `/oauth/authorize` and `/oauth/token` endpoints, with `/oauth/token` throwing the `Invalid CSRF token found for http://localhost:9999/uaa/oauth/token` error.
To understand the relationship between the above control flow chart and the `/oauth/authorize` and `/oauth/token` endpoints, you can compare the above flowchart side by side with the chart for the single factor flow at the official spec in a separate browser window. The **SECOND PASS** above simply runs through the steps from the one-factor official spec a second time, but with greater permissions during the **SECOND PASS**.