Solr is the popular, blazing-fast, open source enterprise search platform built on Apache Lucene™.
Apache Solr is a web application built around Lucene with all kinds of goodies.
The main difference between Solr and Elasticsearch is that Solr is a completely open-source search engine. Whereas Elasticsearch though open source is still managed by Elastic's employees. Solr supports text search while Elasticsearch is mainly used for analytical querying, filtering, and grouping.
Solr is an open-source search platform which is used to build search applications. It was built on top of Lucene (full text search engine). Solr is enterprise-ready, fast and highly scalable. The applications built using Solr are sophisticated and deliver high performance.
@darkheir: Lucene and Solr are 2 differents Apache projects that are made to work together, I don't understand what is the aim of each project.
Solr uses Lucene under the hood. Lucene has no clue about the Solr API.
Lucene is a powerful search engine framework that lets us add search capability to our application. It exposes an easy-to-use API while hiding all the search-related complex operations. Any application can use this library, not just Solr.
Solr is built around Lucene. It is not just an http-wrapper around Lucene but has been known to add more arsenal to Lucene (archived). Solr is ready-to-use out of box. It is a web application that offers related infrastructure and a lot more features in addition to what Lucene offers.
@darkheir: Lucene is used to create a search index and Solr use this index to perform searches. Am I right or is this a totally different approach?
Lucene doesn't just create the Index for the consumption by Solr. Lucene handles all the search related operations. Any application can use the Lucene framework.
Examples are Solr, Elastic Search, LinkedIn (yes, under the hood), etc..
Check out this article: Lucene vs Solr
UPDATE (6/18/14)
When to use Lucene?
When to use Solr?
NOTE: I don't mean that Solr is hard to customize. Solr is very flexible and provides a lot of pluggable API points, allowing you to throw-in your code.
There are people, falling under 'have to use Lucene' camp, but still prefer Solr to plain Lucene as it's easy to use. However, they never restrain themselves from customizing Solr to the maximum extent.
BTW, I see that there are more resources on Solr (4.x) than Lucene (4.x).
Lucene is a low level Java library (with ports to .NET, etc.) which implements indexing, analyzing, searching, etc.
Solr is a standalone pre-configured product/webapp which uses Lucene. If you prefer dealing with HTTP API instead of Java API, Solr is for you. Solr has also got some extra features on top (e.g. grouping).
A simple way to conceptualize the relationship between Solr and Lucene is that of a car and its engine. You can't drive an engine, but you can drive a car. Similarly, Lucene is a programmatic library which you can't use as-is, whereas Solr is a complete application which you can use out-of-box.
Source: Lucene-vs-solr - Lucene Tutorial
Solr is built on top of lucene to provide a search platform.
Search platform in the following layers from bottom to top:
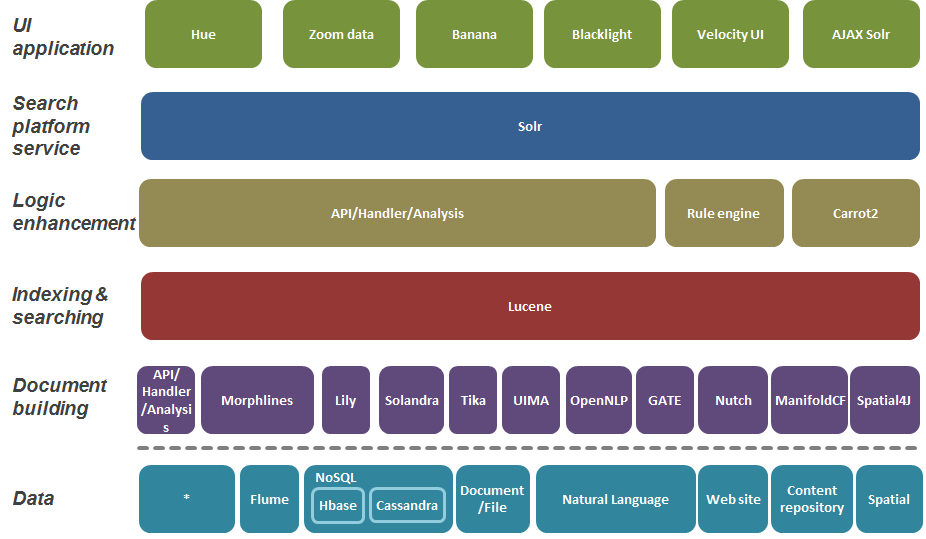
Reference article : Enterprise search
SOLR is a wrapper over Lucene index.
It is simple to understand: SOLR is car and Lucene is its engine. You just need to know how to drive car (SOLR) and also need to know few things of engine (Lucene) in case if there will be any issue in your car engine.
Have a safe drive :)
If you love us? You can donate to us via Paypal or buy me a coffee so we can maintain and grow! Thank you!
Donate Us With