What is ffpdm in HTML ?
I sometimes see it in a website's source code as an attribute for HTML or INPUT tag.
For example you can see it in jsSHA - SHA Hashes in JavaScript
Thank you in advance .
The one PDM I know is Precedence Diagramming Method and FF looks like Finish to Finish. Maybe I am wrong but If I am right the explanation is following...
A Precedence Diagramming Method (PDM), which is sometimes also known as the Activity on Node (AON) Diagramming Method, is a graphical representation technique, which shows the inter-dependencies among various project activities. This diagramming method is used to draw the project schedule network diagrams – for example the Critical Path Network Diagram and the Critical Chain Network Diagram.
I hope that you may have heard about another less commonly used technique in diagramming methods – the Activity on Arrow (AOA) diagramming method, which is a special case of the Precedence Diagramming Method. In AOA, all dependencies are Finish to Start, and the duration is shown on arrows. That is why, this diagramming method is known as the Activity on Arrow (AOA) diagram. PERT is an example of AOA diagram.
Activity on Arrow (AOA) diagram emphasizes on milestones (events),
and the PDM diagram emphasizes the tasks.
The main benefit of Precedence Diagramming Method (PDM) is that it shows the activity dependencies, and it also an important communication tool for stakeholders.

(source: netdna-cdn.com)
The Precedence Diagramming Method (PDM) consists of rectangles known as nodes, and the project activities are shown in these boxes. These rectangular boxes are connected to each other through an arrow to show the dependencies; therefore, these diagrams are also known as the Activity on Node (AON) diagrams.
The Precedence Diagramming Method uses four types of dependencies. Those dependencies are as follows:
In this type of dependency, the second activity can not be started until the first activity completes. This type of dependency is the most commonly used dependency in the diagramming techniques.
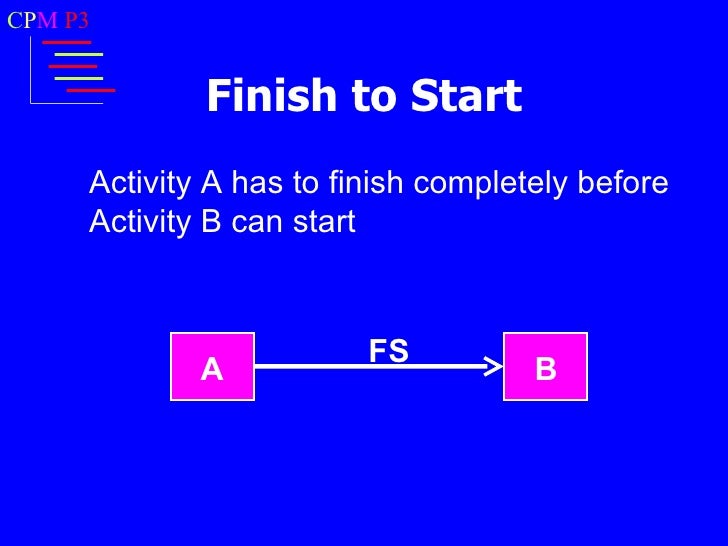
For example: to paint a wall first you need to build a wall. In this case, first activity is building the wall and second activity will be painting. You can not start painting the wall unless the wall is ready.
Here, the second activity cannot be finished until the first activity finishes; in other words, both activities should finish simultaneously.
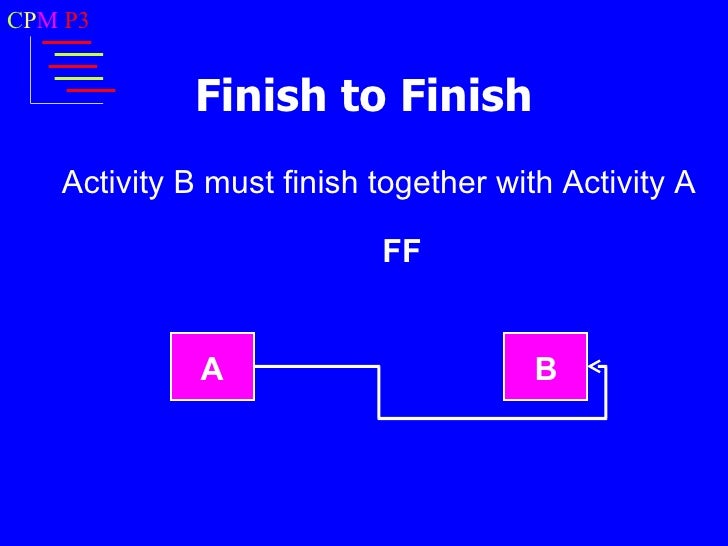
For example: let us say that you coding a program for a client, and the client is providing you the characteristics of the program. In this case you can not finish coding for your program until the client gives you his complete requirements. Here, both activities should finish simultaneously.
Here, the second activity cannot be started until the first activity starts; both activities should start simultaneously.
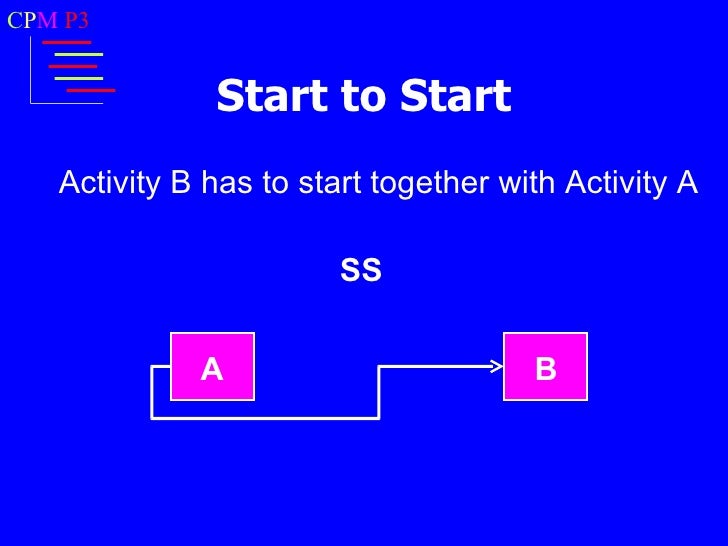
For Example: Suppose you have to apply primary coating on the wall. To apply the coating, you also need to clean the wall. Therefore, one team will start cleaning the wall and second team will paint it. Both activities can be started at the same time.
In this type of dependency, the second activity cannot be finished until the first activity starts.

For example: let us say you have to move into a new home, and your old home has to be demolished. In this case, you can not move to your new home until it is ready. Hence, the second activity (construction of new home) must be finished before the first activity starts (you start moving into new home); i.e. if you are moving into your new home, you cannot start vacating your old home until the new house is completely ready.
If you love us? You can donate to us via Paypal or buy me a coffee so we can maintain and grow! Thank you!
Donate Us With